An investment firm or fund is a partnership, trust or corporation that “pools” money from shareholders and invests it in the appropriate security instruments and multiply investment money.
The working of investment firms is based on few collective features. They are discussed in detail.
1) Close-Ended Structure
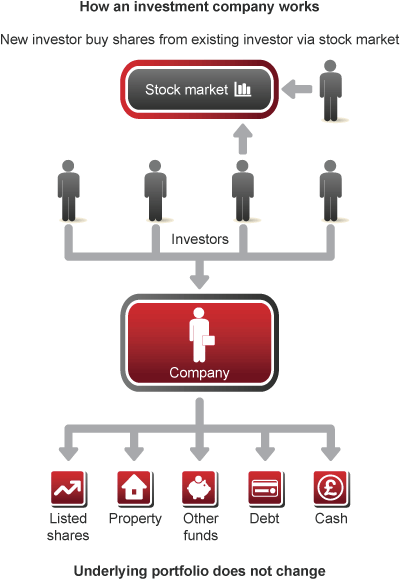
Investment management firms have a close-ended structure which means that they issue a fixed number of shares at certain time-frame. These shares are traded on the stock market.
In this structure, the fund managers invest in less liquid assets such as commercial properties, venture capital and private equity, to deliver long-term sustained results.
2) Board of Directors
An independent board of directors exists in all management firms as their role and responsibility is to protect the interest of the investor.
The board of directors meets a couple of times every year to review the investment company’s performance, and offer advice.
3) Stock Exchange Listed
In order to be operating, management companies need to be listed on the stock exchange. They can be listed on more than one stock exchange.
4) Shareholder Rights
By buying shares in best investment firms, the shareholder receives certain rights which can be exercised as and when the need arises.
The shareholders can participate in annual general meetings (AGM), select or change the board of directors, motion tables and motion extraordinary general meetings (EGM).
5) Multiple Share Classes
Depending on the business model of the firms, they can either issue ordinary share or if it’s a split capital investment company, it can issue multiple classes of share.
The earlier one is a traditional company where the shareholder money earns dividends over a long period of time.
In the later one, fund managers invest the money in various instruments to generate an income for shareholders.
6) Selective Investment
Financial companies have the right to decide where they want to invest the shareholders money.
They can invest in any segments such as various business sectors, companies, and global companies or choose to invest in a particular geographic region.
Special investment firms exist such as hedge funds, venture capital trusts, property firm and private equities to handle selective models.
Sometimes certain firms invest in another firm too.
7) Fund Management
The board of directors is entrusted with the task of selecting fund managers. The fund managers are tasked to decide the day-to-day working of funds, to decide what to sell and what to buy.
The fund managers are a part of the external management group, hired to function within a certain management firm, and these groups aren’t limited to only one institution.
If it’s a small company, it’s often self-managed because the board of directors hires in-house fund managers directly.
8) Investment Gearing
‘Gearing’ is the process where the firm borrows from the outside for additional investments.
The purpose of additional investments is to return shareholders money with dividends and make profit in between.
Such borrowed funds are invested in attractive stocks or provable long-term plans. Moreover, another advantage is they borrow at lowered interest rates than others.
The decision to engage in ‘gearing’ rests with the board of directors and the fund manager.
List of Top 10 Investment management firms in the World
Here is the global top 10 list of the investment management firm, along with a brief about their business model or investment banking services.
1) Goldman Sachs [1869 – USA]
Goldman Sachs engages with institutional clients in the fields of investment management, securities, global investment banking, asset management, prime brokerage to corporations and governments, mergers and acquisitions advice, underwriting services and more.
A primary dealer of the US Treasury, Goldman Sachs also deals in private equity and is a recognized premier investment bank in the world.
Investment banking constitutes 17% of its revenues.
2) Morgan Stanley [1935 – USA]
Morgan Stanley operates in investment management, institutional securities and global wealth management segments.
It offers products and services to governments, corporations, financial institutions and public customers.
Since the 1990s, they have served as lead underwriter for various technology-based companies IPOs like VeriSign and Dolby Laboratories, and have played a dominant role in technology investment banking.
3) JPMorgan Chase & Co. [2000 – USA]
A relatively new financial firm compared to others, JPMorgan Chase & Co. is a financial services holding firm and a multinational banking entity.
Based on composite ranking carried out by Forbes, it is the world’s third-largest public firm and has the second-largest hedge fund unit in USA.
JPMorgan Chase & Co. or the JPMorgan brand operates under various segments like private wealth management, security services, treasury, private banking, asset management, credit card services, retail banking, and commercial banking.
4) Bank of America Merrill Lynch [2009 – USA]
Merrill Lynch is the investment banking division of Bank of America, formed after the acquisition of Merrill Lynch & Co. in 2009.
The investment banking division operates globally, offering services in trading, risk management, debt capital markets, liquidity management, equity capital markets, mergers and acquisitions and lending.
5) Deutsche Bank AG [1870 – Germany]
With a pan-global presence, Deutsche Bank has 21% foreign exchange market share, according to 2009 reports.
Deutsche Bank is a global financial services and banking entity, working with government and private clients for mergers and acquisitions, corporate finance, retail banking, transaction banking, fund management, debt and equity, risk management and derivatives.
6) Citigroup Inc. [1812 – USA]
The merger of Citicorp and Travelers Group led to the formation of Citigroup Inc. in 1998. In the US, it is the third-largest assets holding bank.
The business model consists of five different divisions: global consumer banking, institutional clients group, Citi ventures, Citi holdings and Spin-offs.
These consists of retail banking, credit cards, commercial banking, real estate mortgages, services to governments and corporations, services to high-net individuals, treasury, securities, trade solutions, issuer businesses, hedge and private equity services, direct custody and hearing, investor services, municipals, debt obligations and more.
7) Credit Suisse Group [1856 – Switzerland]
The Credit Suisse Group operates various financial services and Credit Suisse Bank. Shared Services Group, Asset Management, Private Banking and Investment Banking are its four divisions.
They follow the bancassurance strategy of offering every necessary financial service under one platform.
Their investment banking solutions is for individuals and company holding more than 50,000 Euros in wealth.
Their investment banking model includes mergers and acquisitions, fixed income, hedge funds, mutual funds, securities and equity products.
Their wealth management model consists of tax planning, estate planning, insurance, philanthropy, managed accounts, real estate, foreign exchange and lending.
8) Barclays Investment Bank [1997 – London]
The investment banking division of Barclays Bank, the Barclays Investment Bank offers risk management and financial services to government, institutions and corporations.
They are the primary dealer of European Government Bonds and US Treasury securities.
Their investment banking and wealth management business is made up of both execution-only and discretionary portfolio management services.
9) UBS AG [1854 – Switzerland]
The Swiss financial services firm offers asset management, wealth management, and investment banking services to institutions, corporations and private clients globally.
According to the 2013 JPMorgan Equity Research, UBS manages over 2.2 trillion Swiss francs in investment assets, making it the largest manager of private wealth assets.
Equities research, credit, precious metals, derivatives, foreign exchange, and other financial products are offered by UBS in their investment banking services.
10) HSBC Holdings PLC [1865 – Hong Kong]
The world’s second-largest bank, HSBC Holdings PLC operates under four business groups.
They are investment banking, wealth management, retail banking and global private banking.
HSBC investment banking caters to institutional and corporate clients, offering cash management, leveraged acquisition finance, payments, trading, corporate banking, foreign exchange, securities and asset management services.
Types of Investment Companies
There are broadly four types of investment companies, offering various financial services.
1) Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)
It is either an Unit Investment Trust (UIT) or an open-end investment firm where the shares are traded on stock exchanges in the intra-day format at market prices.
The ETF maintains professional management and diversified portfolio, and they trade in the market like equity security.
2) Unit Investment Trust (UIT)
UIT investment companies buy and secure a fixed portfolio made with bonds and stocks.
They are externally managed because the share units are sold to investors who keep receiving dividends as long as they are holding the units.
The units mention a date of expiry, based on the nature of the investment instrument.
3) Closed-End Fund
This is where a fixed number of shares are issued in the stock market and they have less liquidity but long-term benefits.
Such funds have clearly underlined objectives and they are managed externally.
4) Mutual Funds
Like closed-end funds, the mutual funds are managed externally too. Here, a professional investment adviser buys security portfolios to reach a specified financial goal of the investor.
Mutual funds are redeemable anytime.
Endnote
The purpose of writing about the working of investment companies is to give you a better idea of how the industry functions.
If you’re looking for an investment banking career, you need to know how it operates to make informed decisions.
Of course, variations will be there based on where you’re recruited but this is the gist.







